Understanding Fainting In Men: A Comprehensive Guide To Causes, Diagnosis, And Management
Understanding Fainting in Men: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Management
Related Articles: Understanding Fainting in Men: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Management
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Fainting in Men: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Fainting in Men: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Management
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1298399-article-img-causes-of-fainting1-5a5520127bb283003773f0c9.png)
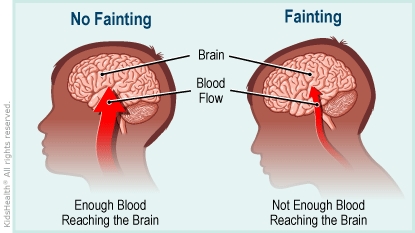
Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain. While it can occur in individuals of any gender, understanding the specific causes and contributing factors in men is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of fainting in men, exploring the underlying mechanisms, common causes, diagnostic approaches, and essential management strategies.
Causes of Fainting in Men
Fainting in men can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from benign physiological responses to serious underlying medical conditions. It is essential to categorize these causes for a comprehensive understanding:
1. Neurocardiogenic Syncope (Vasovagal Syncope):
This is the most common type of fainting, accounting for approximately 50% of cases. It is characterized by a sudden drop in blood pressure and heart rate, triggered by a variety of stimuli, including:
- Emotional Stress: Fear, anxiety, pain, or even strong emotions like excitement can trigger vasovagal syncope.
- Pain: Intense pain, particularly in the extremities, can lead to a drop in blood pressure and fainting.
- Prolonged Standing: Standing for extended periods, especially in hot environments, can cause blood to pool in the legs, reducing blood flow to the brain.
- Stimuli: Certain sights, sounds, or smells can trigger vasovagal syncope in susceptible individuals.
2. Orthostatic Hypotension:
This condition occurs when blood pressure drops significantly upon standing, leading to dizziness and fainting. It can be caused by:
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to reduced blood volume, causing orthostatic hypotension.
- Medications: Certain medications, including diuretics, antihypertensives, and antidepressants, can lower blood pressure and contribute to orthostatic hypotension.
- Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction: Conditions affecting the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood pressure, can lead to orthostatic hypotension.
3. Cardiac Syncope:
This type of fainting is caused by problems with the heart, including:
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats, such as bradycardia (slow heart rate) or tachycardia (fast heart rate), can disrupt blood flow to the brain.
- Valve Problems: Faulty heart valves can impede blood flow, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the brain.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Blockages in the coronary arteries can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, potentially causing fainting.
4. Other Causes:
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels can cause fainting, particularly in individuals with diabetes.
- Hyperventilation: Rapid, deep breathing can lead to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels in the blood, causing dizziness and fainting.
- Seizures: Some types of seizures can mimic fainting, but they are characterized by muscle spasms and loss of bladder control.
- Stroke: While rare, a stroke can cause sudden weakness, numbness, and fainting.
Diagnosis of Fainting in Men
Diagnosing the cause of fainting requires a thorough medical evaluation, which typically involves:
- Medical History: A detailed history of the fainting episodes, including triggers, symptoms, and associated conditions, is crucial.
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical exam, including blood pressure and heart rate measurements, can help identify potential causes.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records electrical activity in the heart, detecting any arrhythmias or other heart problems.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart, revealing any structural abnormalities or valve problems.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn for 24-48 hours can detect intermittent heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Tilt Table Test: This test simulates the effects of standing, helping to diagnose orthostatic hypotension and vasovagal syncope.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can rule out conditions like hypoglycemia, anemia, and electrolyte imbalances.
Management of Fainting in Men
Treatment for fainting depends on the underlying cause. Some common approaches include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: For vasovagal syncope, avoiding triggers like prolonged standing, dehydration, and emotional stress can be helpful.
- Medications: Medications like beta-blockers, fludrocortisone, and midodrine can help manage orthostatic hypotension.
- Pacemaker: For certain types of bradycardia, a pacemaker can regulate the heart rate.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair heart valve problems or coronary artery disease.
- Counseling: Cognitive behavioral therapy can help manage anxiety and stress, which can contribute to vasovagal syncope.
FAQs by Fainting Causes in Men
1. Neurocardiogenic Syncope (Vasovagal Syncope):
-
Q: What are the typical symptoms of vasovagal syncope?
- A: Symptoms may include nausea, sweating, dizziness, blurred vision, a feeling of warmth, and a rapid heartbeat before fainting.
-
Q: Is vasovagal syncope dangerous?
- A: In most cases, vasovagal syncope is not life-threatening. However, it can be dangerous if it occurs while driving or engaging in other activities that require alertness.
-
Q: Can I prevent vasovagal syncope?
- A: Avoiding triggers like prolonged standing, dehydration, and emotional stress can help reduce the risk of vasovagal syncope.
2. Orthostatic Hypotension:
-
Q: What are the symptoms of orthostatic hypotension?
- A: Symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, and fainting upon standing.
-
Q: How is orthostatic hypotension diagnosed?
- A: A tilt table test can help diagnose orthostatic hypotension by simulating the effects of standing.
-
Q: What are the treatment options for orthostatic hypotension?
- A: Treatment options include increasing fluid intake, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and taking medications like fludrocortisone and midodrine.
3. Cardiac Syncope:
-
Q: What are the symptoms of cardiac syncope?
- A: Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fainting.
-
Q: How is cardiac syncope diagnosed?
- A: Diagnosis typically involves an ECG, echocardiogram, and Holter monitor to assess heart function.
-
Q: What are the treatment options for cardiac syncope?
- A: Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medications, pacemakers, or surgery.
4. Other Causes:
-
Q: How is hypoglycemia diagnosed?
- A: Blood sugar testing can confirm low blood sugar levels.
-
Q: How is hyperventilation diagnosed?
- A: A medical professional can assess breathing patterns and confirm hyperventilation.
-
Q: How are seizures diagnosed?
- A: Diagnosis typically involves a neurological examination, electroencephalogram (EEG), and medical history.
Tips by Fainting Causes in Men
1. Neurocardiogenic Syncope (Vasovagal Syncope):
- Tip: If you experience a vasovagal syncope episode, lie down with your legs elevated to improve blood flow to the brain.
- Tip: Practice deep breathing exercises to help regulate heart rate and blood pressure.
- Tip: Avoid triggers like prolonged standing, dehydration, and emotional stress.
2. Orthostatic Hypotension:
- Tip: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to prevent dehydration.
- Tip: Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can worsen orthostatic hypotension.
- Tip: Sit or lie down if you feel dizzy upon standing.
3. Cardiac Syncope:
- Tip: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting.
- Tip: Follow your doctor’s recommendations for medications and lifestyle modifications.
4. Other Causes:
- Tip: If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
- Tip: Practice relaxation techniques to manage anxiety and hyperventilation.
Conclusion by Fainting Causes in Men
Fainting in men can be caused by a wide range of factors, from benign physiological responses to serious underlying medical conditions. It is crucial to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. By understanding the various causes, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies, men can take proactive steps to address fainting episodes and improve their overall health and well-being. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing complications and ensuring a positive outcome.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Fainting in Men: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!